Associated Illnesses: EDS
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome - (EDS) is a group of inherited (passed from parent to child) connective tissue disorders. It is caused by mutations in genes encoding connective tissue proteins. The most prominent features are joint hyper-mobility, skin hyper extensibility, changes in the walls of the blood vessels and tissue fragility. This results in easy bruising and abnormal scarring. There are six major classifications of EDS. They are classic, hyper-mobility, vascular, kyphoscolitic, arthrochalasia and dermatosparaxis. The hyper-mobility type is the most common form of EDS followed by the classical type and vascular type.
Many children who develop CRPS have undiagnosed EDS.
EDS is a multisystem disorder.
EDS is a
- Chronic pain disorder
- Chronic fatigue disorder
- Gastrointestinal disorder
- Chronic headache disorder
- Causes pelvic dysfunction
- Causes cardio-vascular dysautonomia
- Causes immune dysregulation
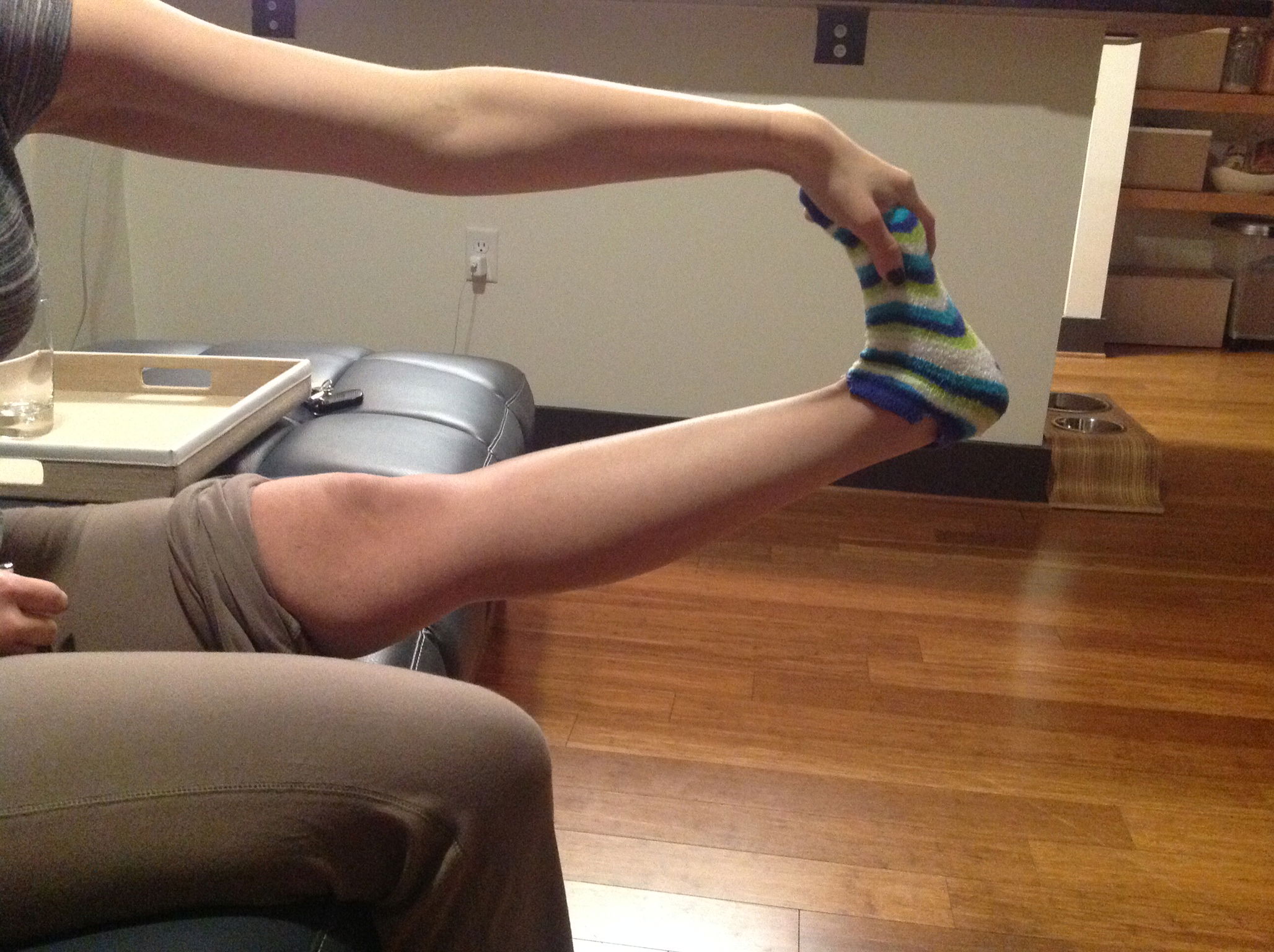
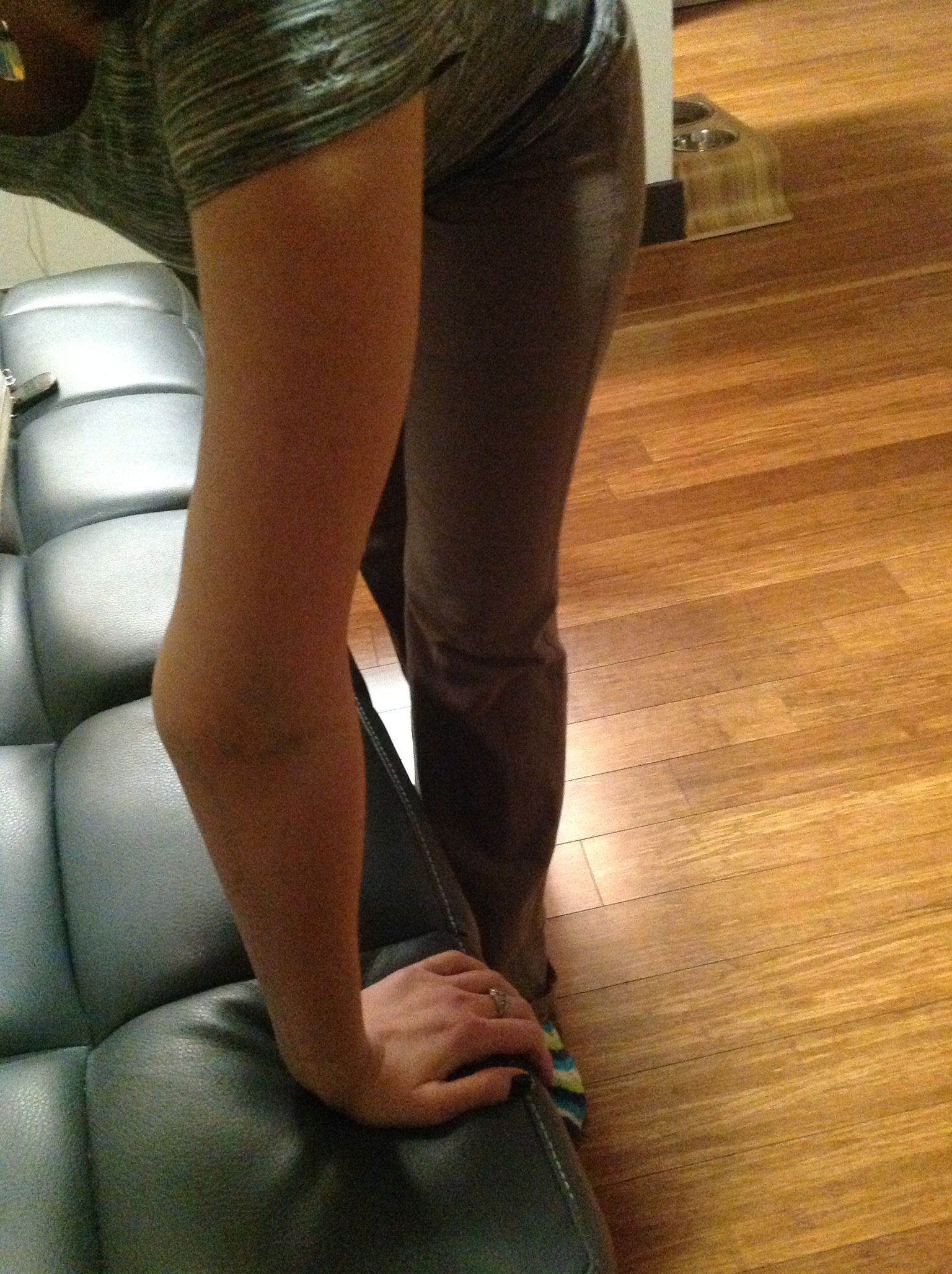
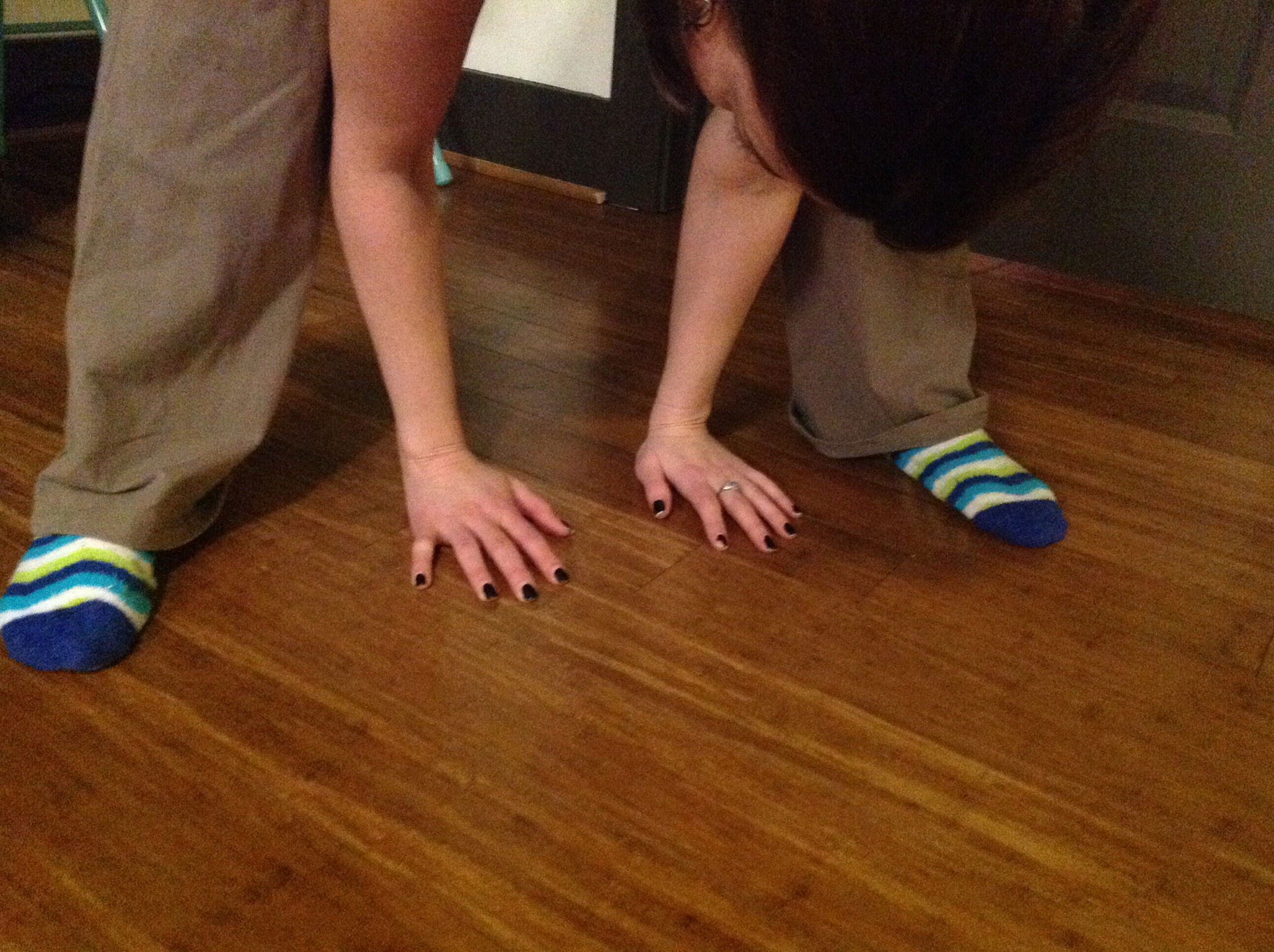
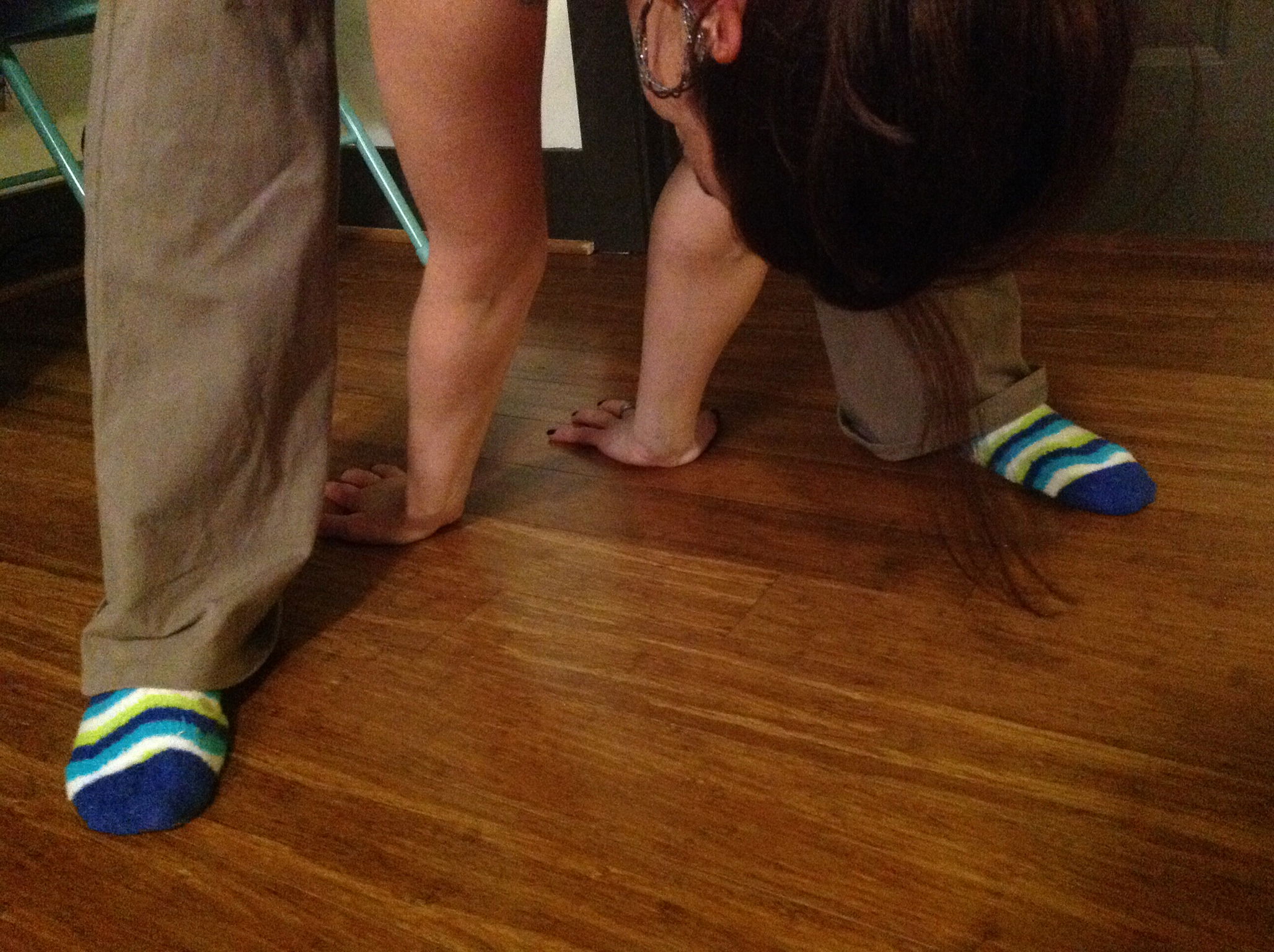
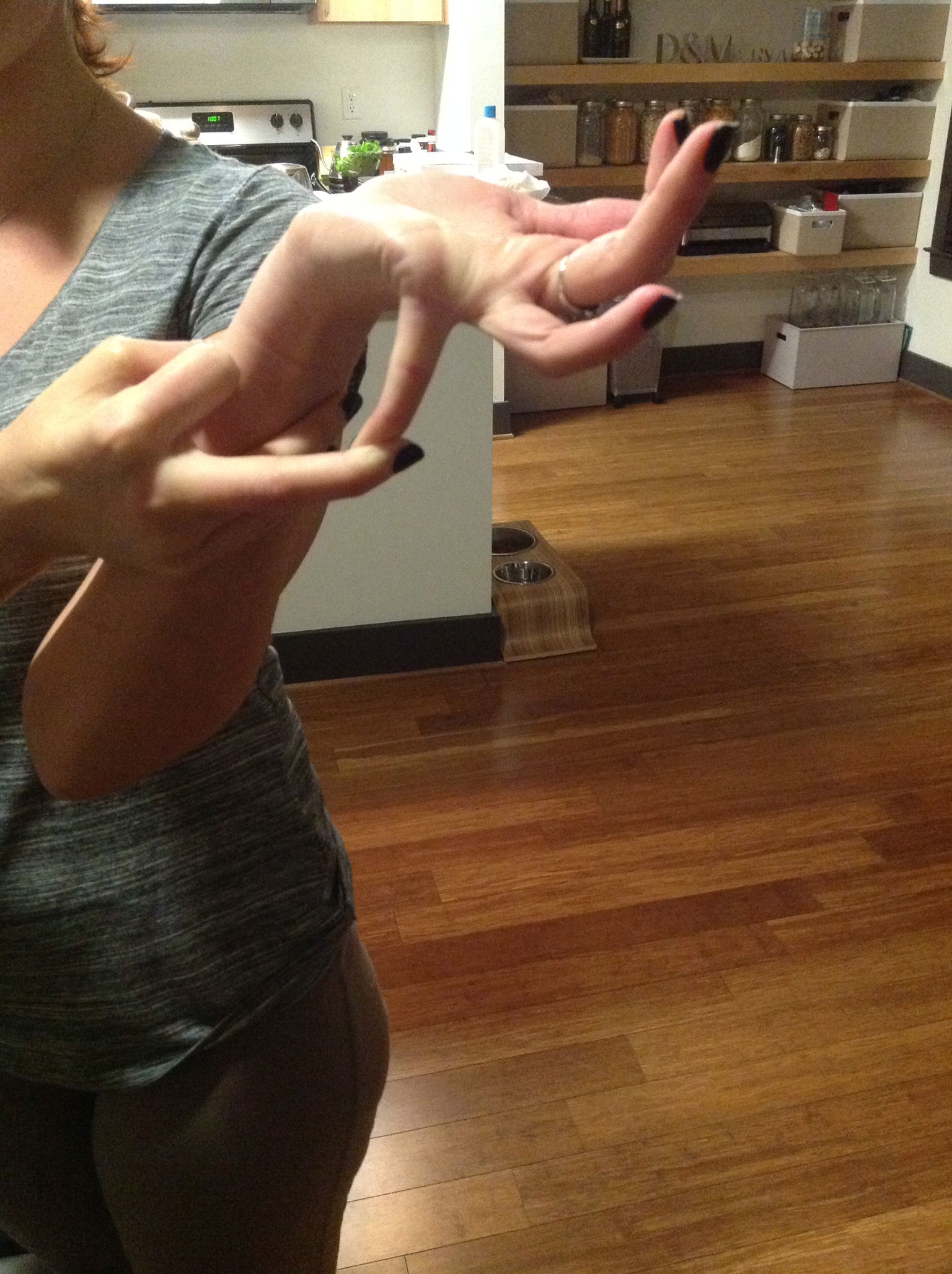
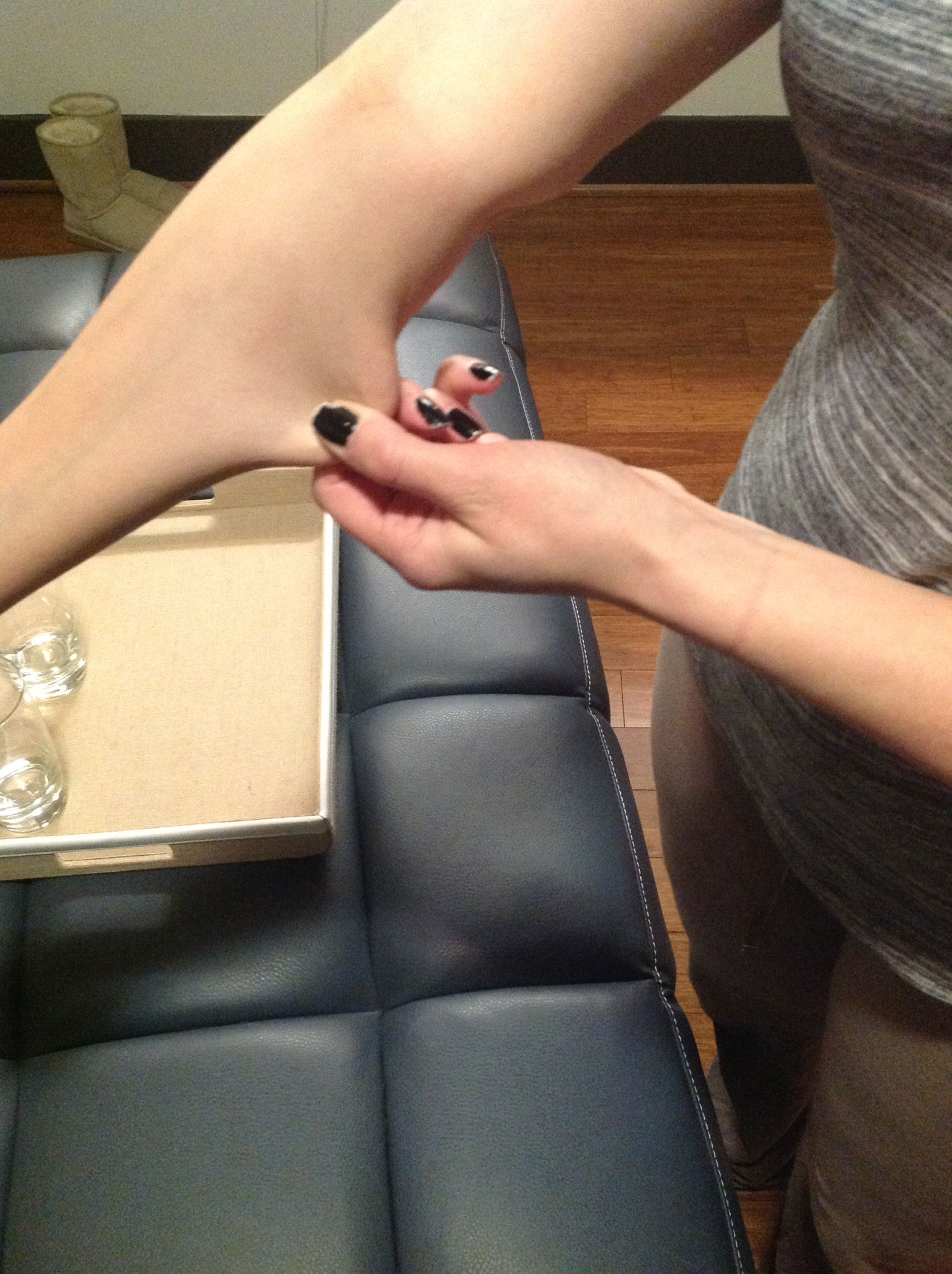
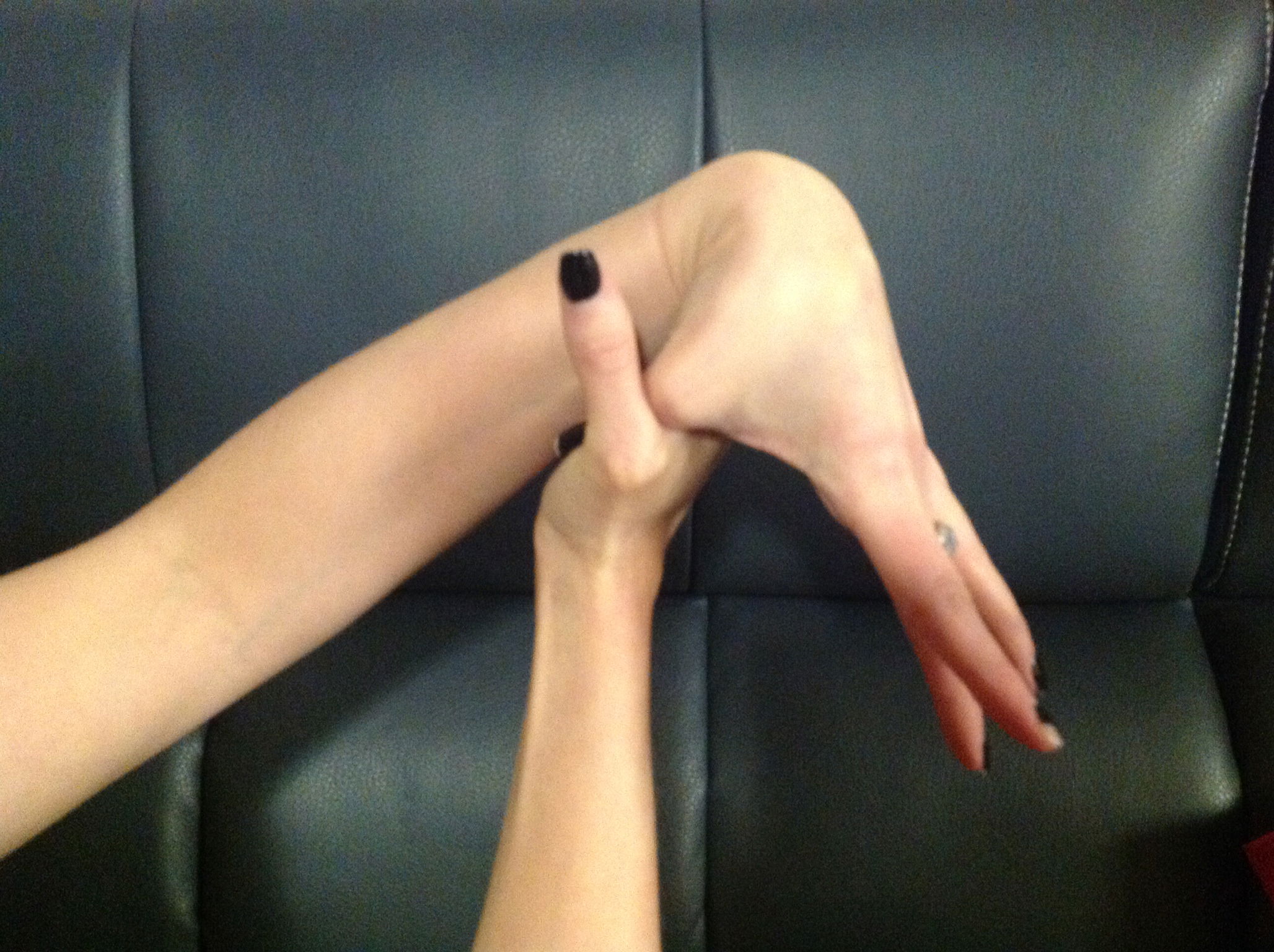
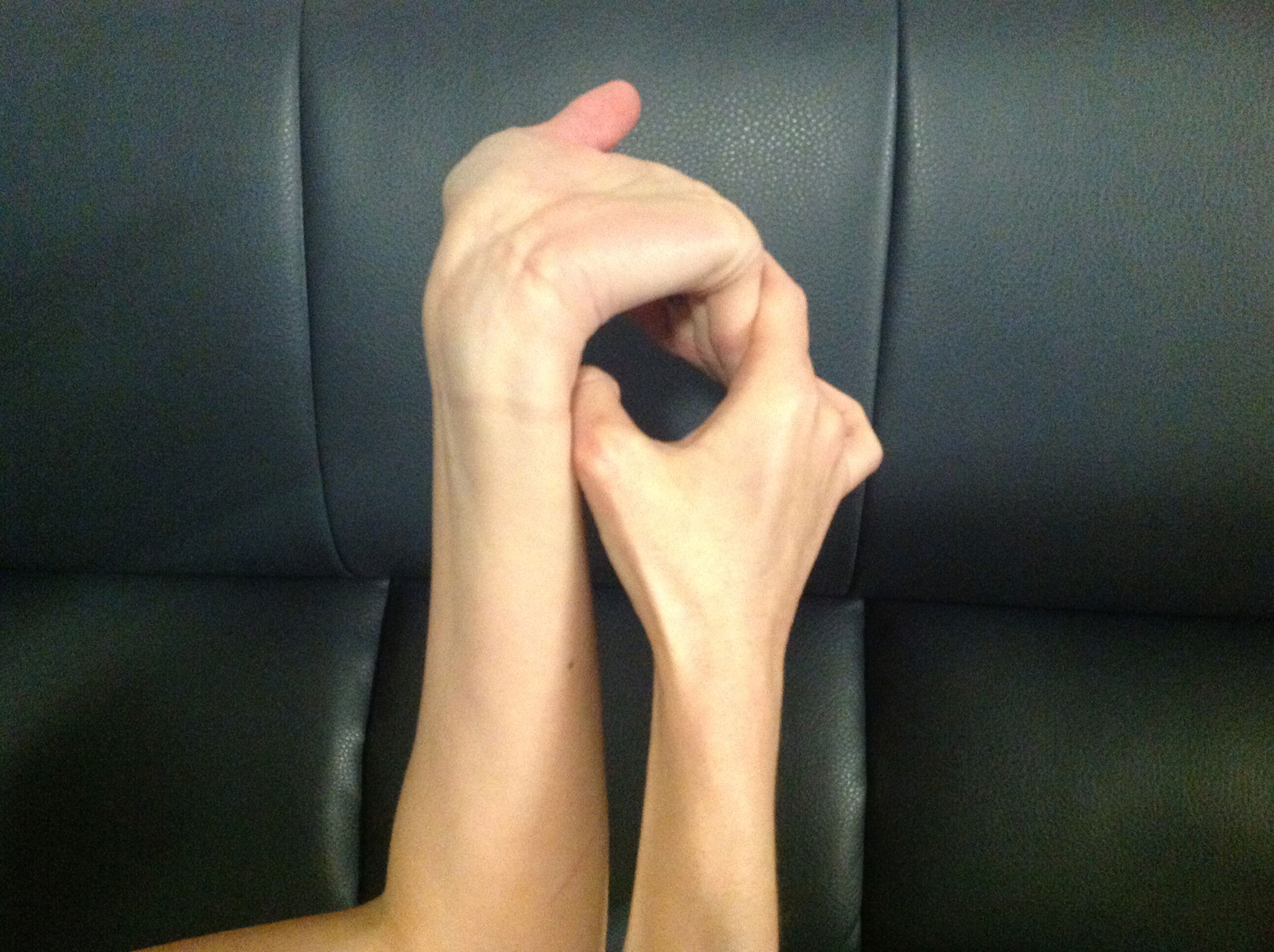
In the case of someone with CRPS, it is repeated injuries caused by hyper-mobility of the joints that often causes the CRPS. Children who develop CRPS often have EDS as an underlying diagnosis. Joint hyper-mobility is determined by what is called the Beighton Scoring System. To be diagnosed with EDS hyper-mobility, you must have a score of four or more.
The Beighton score is calculated as follows:
1. One point if while standing forward bending you can place palms on the ground with legs straight
2. One point for each elbow that bends backwards
3. One point for each knee that bends backwards
4. One point for each thumb that touches the forearm when bent backwards
5. One point for each little finger that bends backwards beyond 90 degrees.